how does a polarimeter distinguish between optical isomers|how to calculate optical polarity : export Polarimeter is the instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light pass through the sample tube containing the solution of sample, and the angle of . webTikToker | Singer | +18 💌
[email protected]
{plog:ftitle_list}
Só Reparos celebra 33 anos de sucesso em Brasília. Publica.
Optical isomerism. Optical isomers are named like this because of their effect on plane polarized light. Simple substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. A solution of one enantiomer rotates the plane of polarisation in a .
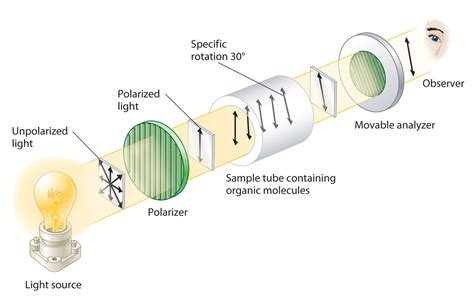
The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter . Polarimeter is the instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light pass through the sample tube containing the solution of sample, and the angle of .
Optical isomers possess identical physical properties (except in some cases they form asymmetric mirror image crystals), with one important exception; a pure optical isomer, or .
The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Monochromatic (single wavelength) light, is polarized by a fixed polarizer . One of the optical isomers will rotate the plane of polarised in the clockwise direction. Whereas the other isomer will rotate it in the anti-clockwise direction. When unpolarised light is passed through a polariser, the light .Simple substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. A solution of one enantiomer rotates the plane of polarisation in a clockwise direction. This enantiomer is known as the (+) form. This type of isomerism is also known as stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism. It is also known as optical isomerism, as chiral compounds rotate plane-polarised light. The .
The property of a compound being able to rotate the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light is called optical activity, and a compound with such activity is labeled as optical active. A stereoisomer that is optical active is also called . Polarimeter principle, designating optical isomers (+/- Convention, D/L Convention, R/S Convention). How to draw Fischer Projection of simple sugars from the.
Because many optically active chemicals such as tartaric acid, are stereoisomers, a polarimeter can be used to identify which isomer is present in a sample – if it rotates polarized light to the .
polarometer optical activity
polarity and optical activity
donatelli hip drop test
Optical isomerism. Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same structural formula but have the atoms arranged differently in space There are two types of stereoisomerism. Geometrical (E/Z) Optical; A carbon atom that has four different atoms or groups of atoms attached to it is called a chiral carbon or chiral centre. Chira comes from a Greek word .The measurement of the optical activity of a substance results in the angle of rotation – also known as the rotation value. A difference is made between the optical rotation and the specific angle of rotation. The optical rotation determines the measured value of the polarimeter, without taking specific physical influences into consideration.The polarimeter is an instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light passes through the sample tube containing the solution of a sample, and the angle of rotations will .
Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. . Thickness of the quartz is selected in such a way that it introduces a path difference of ’A/2 between ordinary and extraordinary ray. . is present in a sample – if it rotates polarized light to the left, it is a levo-isomer, and to the right, a . Molecules with a chiral centre exist as optical isomers; These isomers are also called enantiomers and are non-superimposable mirror images of each other; The major difference between the two enantiomers is that one of the enantiomers rotates plane polarised light in a clockwise manner and the other in an anticlockwise fashion. The enantiomer that .A molecule will exhibit optical isomerism if it contains a chiral centre/ an asymmetric carbon atom - in other words, if it contains a carbon atom with 4 different groups attached.Due to this property, these types of molecules have a mirror image that is non-superimposable upon itself.This means that you cannot map one molecule onto the other (unless you break some .
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Notice that in the structural isomers, there was some difference in the connection of atoms. For example, 1-butene has a double bond followed by two single bonds while 2-butene has a single bond, then a double bond, then a single bond. . They are optical isomers because they have the same connectivity between atoms but a different arrangement .
This video gives a good overview of this topic. Before you begin reading this section, review section 1.5, which contains an introduction to isomerism.. Constitutional isomers. IUPAC defines constitutional isomerism as “isomerism between structures differing in constitution and described by different line formulae e.g. CH 3 OCH 3 and CH 3 CH 2 OH.”” Recall that there .
Formation of Racemic Mixtures. A racemic mixture is a 50:50 mixture of both the (+) enantiomer and the (-) enantiomer of an optical active substance.. This happens because there is an equal chance of forming each enantiomer in a chemical reaction.. A racemic mixture is not optically active because the effects of the (+) and (-) isomers cancel each other out. .The Difference Between Enantiomers on the Molecular Scale. A strategy, which is based on the Latin terms for left (sinister) and right (rectus), has been developed for distinguishing between a pair of enantiomers.Arrange the four substituents in order of decreasing atomic number of the atoms attached to the stereocenter. (The substituent with the highest atomic number gets the . Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample.
Optical isomerism is a case where the isomers display identical characteristics in terms of molecular weight as well as chemical and physical properties. However, they differ in their effect on the rotation of polarized light. . The difference between chiral and achiral molecules can be explained on the basis of the plane of symmetry. If all .Optical Rotation (Optical Activity) - When a beam of plane-polarized light propagates through a quartz crystal along the optic axis, the plane of polarization steadily turns about the direction of the beam. . In an instrument called a polarimeter, optical rotation is measured. A linear association occurs between the rotation observed and the .Optical isomers share all of their physical and chemical properties except one: the direction that they rotate plane-polarized light. While this may seem like a trivial difference, optical isomerism can have a major effect on the behavior . Enantiomers Have Identical Physical Properties Except for Optical Rotation “The Third Property Brother”: meso . This is really helpful but could you include regioisomers vs true constitutional isomers please? Also the .
Plane polarized light will rotate in different directions when passing through different stereo isomers (from a pair of enantiomers). A polarimter measures .
Sample #1 and #2 are straightforward.. Sample #3 is for a mixture with equal amount of two enantiomers, and such mixture is called racemic mixture or racemate.Racemic mixtures do not rotate the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light, that means racemic mixtures are optical inactive and have the observed rotation of zero!This is because that for every molecule in the .Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity.Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking .
Topic 5 – Stereochemistry and optical isomers Isomerism Recap Classification of isomers Stereoisomers - enantiomers Chiral molecules (optical isomers) A molecule is chiral if it is not superimposable upon its mirror image A pair of molecules which are not identical but are mirror images of each other are called enantiomers The D-L system corresponds to the configuration of the molecule: spatial arrangement of its atoms around the chirality center.. While (+) and (-) notation corresponds to the optical activity of the substance, whether it rotates the plane of polarized light clockwise (+) or counterclockwise (-).. D-L system tells us about the relative configuration of the molecule, .
When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in a different direction on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult. . sequence is lower at the first point of difference. In the example shown above this would be C. The .
The angle by which the plane polarised light is rotated is measured by an instrument called polarimeter. Such (+) and (–) isomers of a compound are called optical isomers and the phenomenon is termed as optical isomerism. Measuring Optical Activity. Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter and depends on several factors, The difference between D and L isomers is the position of –OH group in the penultimate carbon atom. D isomer and L isomer are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Difference Between L and D Isomers Definition.A polarimeter is an instrument for measuring the rotation of plane polarised light by a solution containing an optically active compound (diagram . e.g. the 3D requirements of a substrate molecule 'docking' into an enzyme or a reaction between optical isomers of different molecules.
Basic Concepts Optical Isomerism. Optical isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism where molecules with the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution) differ only in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space. This difference arises due to the presence of chirality in the molecules, making them non . It is also known as optical isomerism, as chiral compounds rotate plane-polarised light. The Polarimeter The polarimeter is a device used to measure the optical activity of organic compounds. To measure the rotation of light by a compound, the polarimeter is first aligned so that its two polarising filters Lecture 3 Lecture notes Page 1
doogee s30 drop test
polarimetry formula
Resultado da Alle utlendinger har lukka gardiner Directed by. Ingvild Søderlind. Awards & Festivals Show all (6) Amanda Awards (Norway) 2020 | 6 nominations .
how does a polarimeter distinguish between optical isomers|how to calculate optical polarity